Are Spaghetti Models Accurate? Unraveling Hurricane Forecasts
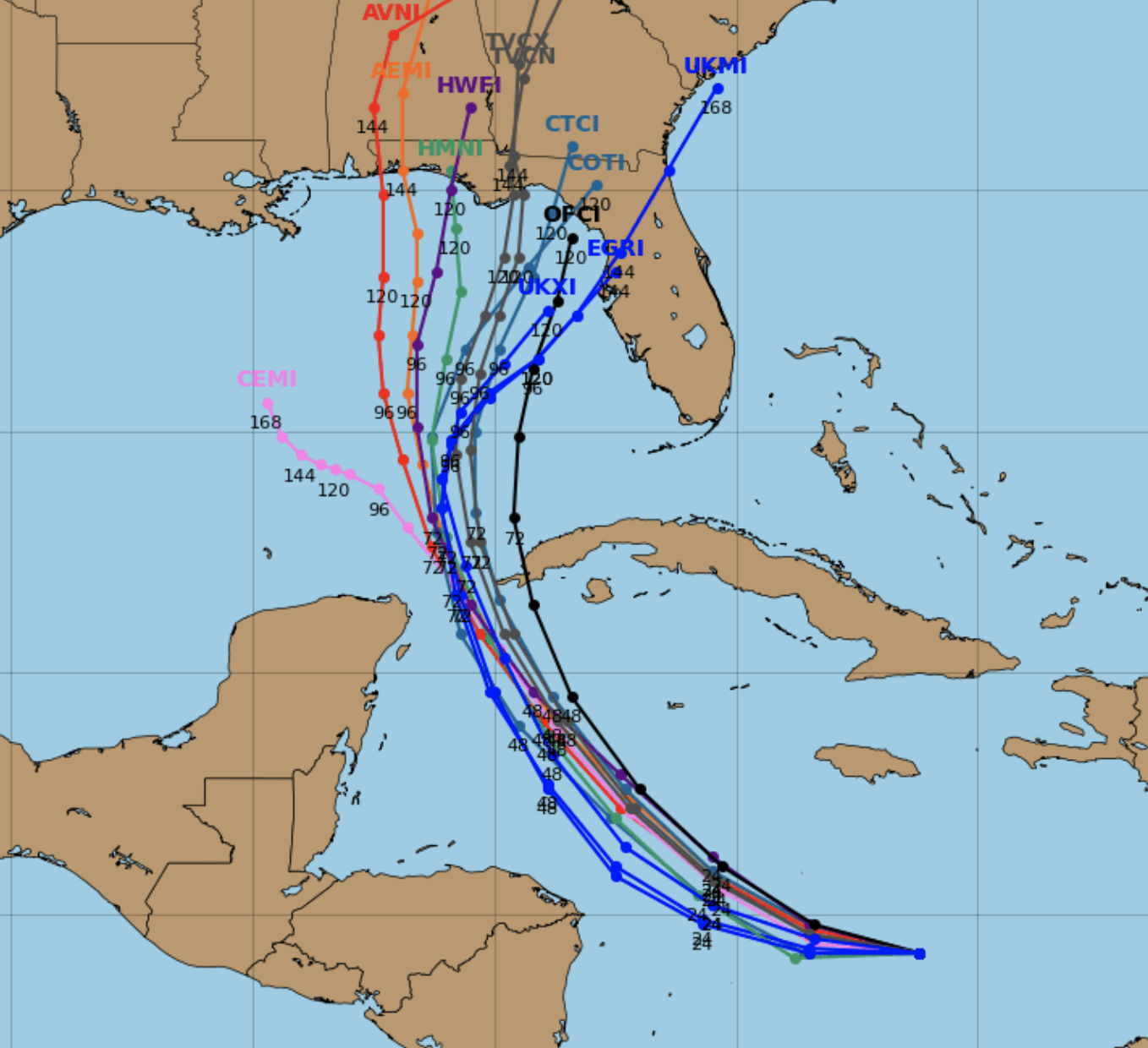
When you see those swirling lines on a weather map during hurricane season, you're looking at what many call "spaghetti models." These visual plots, which frankly look a bit like a plate of pasta, show us the possible paths a tropical storm or hurricane might take. It's a question many folks ask, "Are spaghetti models accurate?" and that, well, is a pretty important thing to consider, especially when big weather events are heading our way.
The very idea of these models is to give us a sense of what could happen, not what definitely will. You see, each line on that plot is a prediction from a different computer model, and when they are all shown together, they can sort of resemble strands of spaghetti. This collective view aims to help us grasp the uncertainty involved in forecasting such powerful weather phenomena, which is actually quite a lot of uncertainty, you know.
This guide is here to help you get a better handle on these fascinating, yet sometimes confusing, predictions. We'll explore what they are, how they work, and most importantly, what to keep in mind when you see them. It's all about understanding their benefits and their limits, so you can interpret the information shown with a bit more confidence, which is really what we all want.
- Howard Morley Oregon
- Sophie Rain Spiderman Erome
- Julie Banderas Nostrils
- Securely Connect Remoteiot P2p Ssh Windows 10
- Tickzoo
Table of Contents
- What Exactly Are Spaghetti Models?
- Why "Spaghetti" Anyway?
- So, Are Spaghetti Models Accurate? The Short Answer
- How to Interpret a Spaghetti Plot
- Spaghetti Models vs. Other Forecasts
- The Role of Technology and Experts
- Key Takeaways for Understanding Spaghetti Models
- Frequently Asked Questions About Spaghetti Models
What Exactly Are Spaghetti Models?
Spaghetti models, or spaghetti plots as some call them, are a very visual way to show predictions for where a tropical cyclone might go. They are basically a collection of different computer models, each one running its own calculations to figure out a storm's potential path. When these individual tracks are laid over each other on a map, they do, you know, sort of look like a bunch of spaghetti strands spread out, which is pretty clever for a nickname, if you think about it.
These models don't just tell us one single path; instead, they offer up a range of possibilities or scenarios. This is actually quite helpful because weather, especially something as complex as a hurricane, is inherently unpredictable. Scientists use these different tools to forecast a storm's behavior, even though the weather itself can be a bit of a moving target, you might say.
Each line you see on a spaghetti plot comes from a different forecast model. There are, in fact, dozens of these models out there, and each one tries to be the best and most precise. They all go about reaching that goal in slightly different ways, which is why their predictions can vary so much, you know, from one line to the next.
- Remoteiot Vpc Ssh Raspberry Pi Download Free Windows
- Viralkand Videos
- Viralcand
- Sone436
- Wwwtickzoo Casinocom
Why "Spaghetti" Anyway?
The name "spaghetti models" really just comes from the way the individual model tracks spread out across the map. Imagine taking a handful of cooked spaghetti and dropping it onto a table; that's the visual effect. It's a very descriptive term that helps people picture what they are looking at, which is pretty neat.
This visual representation is quite effective because it instantly communicates that there isn't just one answer. It shows us the range of potential outcomes, making it clear that forecasting these powerful storms is not a simple, single-line prediction. It’s a way of showing the uncertainty, which is always a big part of weather forecasting, too.
So, Are Spaghetti Models Accurate? The Short Answer
To give you the best answer possible, it's really impossible to make a blanket statement about how accurate these plots are. You see, you can show a spaghetti plot of any set of models, and the reliability of the information shown truly depends on how good those individual models are. It's not a simple "yes" or "no" answer, which is a bit frustrating, but that's how it is, you know.
Spaghetti models, like all weather forecasts, come with a certain amount of uncertainty. They are not infallible, and there are always going to be unknowns. While they offer valuable guidance, they are not always spot-on in predicting the exact path of hurricanes and tropical storms, so you have to keep that in mind.
The Starting Point Matters
A very important thing to remember is that a model is usually most accurate right at its point of origin. As time goes on, the model's accuracy tends to decrease. If that initial point isn't accurate, then the results down the line can end up being a rather inaccurate model overall, which can be a real problem.
This means that the quality of the initial data fed into the models is incredibly important. Without good, precise starting information, even the most advanced computer models will struggle to give reliable long-range forecasts. It's like building a house; if the foundation isn't solid, the rest of the structure will have issues, you know.
Not All Models Are the Same
To the untrained eye, it might seem like all models are created equal, but they most certainly are not. There are many different spaghetti models, and each one tries to be the most accurate. They each have their own way of doing things, their own strengths and weaknesses, which is pretty interesting, if you think about it.
Understanding which spaghetti model might perform better in a given situation is a very complex question. Experts say that no single model is the absolute best all the time. Instead, meteorologists usually look at the average of them all to help inform their forecast, which seems like a sensible approach, too.
How to Interpret a Spaghetti Plot
Before you even try to read a spaghetti plot, it's good to know a few things. These models offer a probabilistic approach to forecasting, which can give you a much more complete picture of the uncertainty involved, especially compared to forecasts that just give you one single outcome. It's about understanding possibilities, not certainties, you see.
The accuracy of these plots can vary quite a bit, and they are most useful when you look at the overall pattern and where the lines tend to group together. It's less about focusing on one individual track and more about seeing the bigger picture. This approach can really help you get a better sense of what might happen, you know.
Look for Clusters, Not Single Lines
When you see a spaghetti plot, don't get too fixated on any single line. Instead, look for where the lines cluster together. These clusters suggest areas where there's a higher agreement among the models, indicating a more probable path for the storm. It's like a consensus among the different predictions, which is very helpful.
If the lines are very spread out, it tells you there's a lot of disagreement among the models, meaning there's a higher degree of uncertainty about the storm's future path. This wide spread suggests that meteorologists have a tougher time narrowing down the possibilities, and that's something important to recognize, too.
The Power of Consensus
The question of which spaghetti model is most accurate when predicting hurricane tracks is quite complex. However, research often points to a consensus approach, especially a simple consensus derived from multiple models, as often outperforming individual models. This means the average of many models tends to be more reliable than any single one, which is pretty neat.
This consensus approach basically takes the collective wisdom of many different models and combines it. It helps smooth out the individual quirks or biases that any one model might have. So, when you see a tight cluster of lines, it's usually a good sign of a more confident forecast, you know.
Freshness Counts
One very important thing to be aware of is that plots like these often include forecasts that are 12 or more hours old. Data that's that old is generally out of date in the fast-moving world of weather forecasting. Always try to look for the most recent model runs to get the best possible information, which is something you really should do.
Weather conditions can change rapidly, and new data is constantly being fed into these models. An older forecast might not account for recent developments in the atmosphere or the storm itself. So, always check the timestamp on the models you are viewing to make sure you are looking at the freshest information available, which is very important.
Spaghetti Models vs. Other Forecasts
Spaghetti models offer a probabilistic way of looking at forecasts. This can provide a more comprehensive view of the uncertainty involved, especially when compared to deterministic forecasts. Deterministic forecasts just give you one single predicted outcome, which might seem simpler, but it doesn't show you the range of possibilities.
Think of it this way: a deterministic forecast might say, "The storm will hit here." A spaghetti plot, on the other hand, says, "The storm might hit anywhere in this general area, with some paths being more likely than others." This difference is quite significant, as it helps you understand the full scope of what could happen, you know.
While spaghetti models are a powerful tool, they do not tell us what will happen in the future. They offer scenarios or possibilities. This distinction is crucial for anyone trying to prepare for a storm. They give you a range of what to expect, allowing for better planning and decision-making, which is really what they are for.
The Role of Technology and Experts
Today's technology has grown vastly, especially with organizations like the NHC (National Hurricane Center). These advances have led to improved climate projections that can be used to help inform policy and planning decisions. It's a continuous process of improvement, which is pretty amazing, too.
Experts, the meteorologists who interpret these models, play a very critical role. As mentioned, they look at the average of all the models to inform their forecasts, because no one model is considered the best for every situation. Each situation needs to be handled uniquely, because one model is not always more accurate than the other, which is a key point.
These scientists use different tools, including spaghetti models, to forecast a storm's behavior, even though weather phenomena are inherently unpredictable. They combine the output from these models with their own experience and knowledge to give us the most accurate forecast possible. Learn more about weather forecasting on our site, and link to this page understanding weather patterns.
For more detailed information on how these models are developed and used, you might find it helpful to consult resources from a trusted weather organization's website, such as a trusted weather information source. They often provide deeper insights into the science behind these predictions, which is very valuable.
Key Takeaways for Understanding Spaghetti Models
So, to bring it all together, understanding spaghetti models means recognizing their strengths and their limits. They are a probabilistic tool, showing a range of potential paths rather than a single, certain outcome. This probabilistic view is actually one of their greatest benefits, as it communicates uncertainty clearly, you know.
Always remember that the accuracy of these models decreases over time, and the quality of the initial data is paramount. Focus on the clusters of lines, which indicate areas of higher agreement among the models, rather than getting caught up in individual tracks. The consensus approach, where meteorologists look at the average of many models, is often the most reliable method.
Also, always check the freshness of the data. Older model runs can be misleading, so seeking out the most recent information is always a good idea. By keeping these points in mind, you can take control of your data and better interpret what these fascinating plots are trying to tell you about potential storm paths, which is pretty powerful.
Frequently Asked Questions About Spaghetti Models
Are spaghetti models always accurate in predicting the path of hurricanes and tropical storms?
While spaghetti models offer valuable guidance, they are not infallible, and uncertainties still exist. They are not always accurate in predicting the exact path, as weather phenomena are inherently unpredictable. They provide scenarios or possibilities, rather than definitive outcomes, which is important to remember.
Which spaghetti model is most accurate when predicting hurricane tracks?
The question of which spaghetti model is most accurate when predicting hurricane tracks is complex. Research suggests that a consensus approach, specifically the simple consensus derived from multiple models, often outperforms individual models. Experts say that no one model is the best; instead, meteorologists look to the average of them all to inform their forecast, which is quite interesting.
How accurate are spaghetti models compared to other forecasting methods?
Spaghetti models offer a probabilistic approach to forecasting, which can provide a more comprehensive view of uncertainty compared to deterministic forecasts. While deterministic forecasts give a single prediction, spaghetti models show a range of possibilities, which helps in understanding the full scope of potential outcomes. This makes them a very useful tool, you know, for showing the uncertainty.
What Is A Spaghetti Model? Understanding Hurricane Forecasting Charts

Hurricane Spaghetti Models: Four Things You Need to Know to Track

How to read a spaghetti model | WLRN